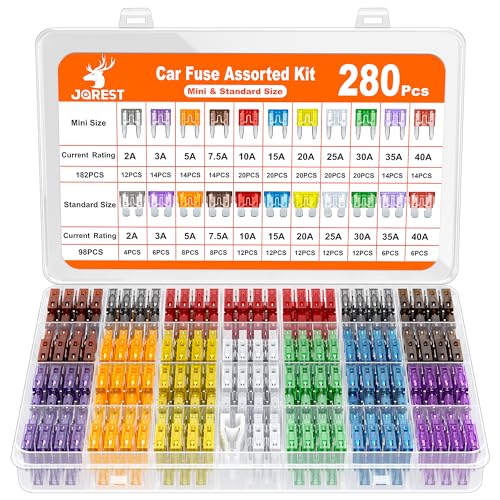
Car Fuses
Why you need this: In disasters, an automotive fuse kit keeps your vehicle running when a blown fuse could strand you, helping your family reach safety.Car Fuses: A Complete Guide to Types, Safety, and Smart Buying
Car fuses are the small, inexpensive components that protect every modern vehicle’s electrical system. These tiny devices are installed in series with circuits so that, if too much current flows, the fuse “sacrifices” itself and opens the circuit before wires overheat or components fail. In plain terms: car fuses prevent bigger, more expensive problems and reduce fire risk.
Why they matter day to day? A single blown fuse can disable essentials like the hazard lights, wipers, defroster, blower motor, charging ports, radio, or even a fuel pump circuit. In everyday mishaps—spilled drinks into the console, a faulty phone charger, a jammed motor—car fuses absorb the damage so you don’t have to replace an entire harness or module. In emergencies, having the right spare fuse can restore critical functions in minutes, helping you stay visible, communicate, and keep the vehicle running safely.
Because they are easy to replace and widely standardized, keeping a small, organized assortment of car fuses in your glovebox or toolkit is a smart preparedness step. Whether you’re commuting, road‑tripping, overlanding, or maintaining a fleet, fuses offer peace of mind at a very low cost.
How It Works
A car fuse contains a calibrated metal element inside a molded body. When current exceeds the fuse’s rating, electrical heating (I²R) causes the element to melt and break the circuit. This rapid interruption prevents wiring and connected components from overheating, which helps avoid costly damage and reduces fire risk. After a fuse operates (“blows”), it must be replaced with a new one of the same type and amperage.
- Where fuses live: Most vehicles have at least one under‑hood fuse box for high‑current circuits and another in the cabin for accessories and comfort features.
- Common types and sizes: Blade fuses dominate modern vehicles and include standard (ATO/ATC), mini, low‑profile mini, micro2, micro3, and maxi. You may also see JCASE, PAL, glass tube, or high‑amperage MIDI/ANL styles for specialty or main feed circuits.
- Ratings and color codes: Automotive fuses are rated in amperes (A). Color coding helps quick identification, but always read the printed number on the fuse body and match what the manufacturer specifies.
- Protection philosophy: A fuse is chosen to protect the wiring first, not to “toughen” the device. Installing a higher‑amp fuse than specified defeats the protection and can be dangerous.
- Time-current behavior: Most automotive blade fuses respond quickly to shorts and sustained overloads. Some larger styles have time-delay characteristics to tolerate brief inrush currents.
- Diagnosis basics: A blown fuse often shows a broken or vaporized element. If unclear, confirm with a test light or multimeter for continuity.
When Car Fuses Help Most
- Natural disasters: After a storm, flood, or blizzard, you may rely on your vehicle for power and mobility. Spare fuses can restore hazard flashers, defrosters, wipers, 12‑volt outlets, or auxiliary lighting if a circuit overloads during harsh conditions.
- Home accidents: Using the vehicle to charge phones during a power outage can stress accessory sockets; a spare fuse gets them working again. Spills in the center console or coins in a socket can short a circuit—new fuses get you back online safely.
- Workplace and fleet: Service vans, trucks, forklifts, and site equipment depend on reliable 12V/24V systems. Having the correct assortment on hand reduces downtime when a powered tool, beacon, or inverter circuit trips a fuse.
- Vehicles on the move: Road trips, towing, and hauling often reveal weak spots in trailer light circuits, cooling fan feeds, or power ports. Spare fuses keep you legal and visible while traveling.
- Outdoor activities: For camping, overlanding, or boating, added accessories (LED lights, fridges, air compressors, radios) raise electrical demand. Properly fused add‑ons and spare fuses ensure safe, dependable power in remote areas.
Strengths, Suitability & Limitations
Strengths
- Inexpensive, lightweight, and easy to store with other roadside essentials.
- Simple to diagnose and replace, even for beginners following the vehicle’s fuse diagram.
- Widely standardized sizes and ratings for most passenger cars, SUVs, trucks, and many powersports or marine applications.
- Prevent larger failures by protecting wiring and sensitive modules from overloads and shorts.
- Fast way to restore critical functions such as hazard lights, wipers, and charging ports.
What It’s Not For
- Not a substitute for proper troubleshooting if a fuse keeps blowing—there is an underlying fault that needs repair.
- Not intended for household AC circuits or non‑automotive systems.
- Not appropriate to “upgrade” amperage to stop a fuse from blowing; doing so removes protection and can lead to fire.
- Not recommended for tampering with safety‑critical circuits (airbags, ABS, high‑voltage hybrid/EV systems). Seek professional service.
Limitations and safety considerations
- Single‑use: once it blows, it must be replaced.
- Environmental factors like heat, vibration, and corrosion can degrade contact quality; reseat fuses firmly.
- Wrong physical size or blade thickness can cause poor contact and intermittent faults.
- Hybrid/EV high‑voltage fuses are not user‑serviceable—do not attempt to replace them yourself.
- Never bypass a fuse with foil or wire, and never install a higher rating than specified.
What to Look For When Buying Car Fuses
Choosing good car fuses is about compatibility, clarity, and quality. Here’s what matters most when you shop:
- Correct types and sizes: Verify what your vehicle uses: standard blade (ATO/ATC), mini, low‑profile mini, micro2, micro3, maxi, JCASE, PAL, glass tube, or high‑amperage MIDI/ANL. Many vehicles mix sizes across different fuse boxes.
- Complete amperage range: Include common values (e.g., 5A, 7.5A, 10A, 15A, 20A, 25A, 30A, 40A for blade; higher for maxi/JCASE/high‑amp). A well‑balanced assortment prevents being stuck with the wrong rating.
- Material and build quality: Look for robust, heat‑resistant plastic bodies with clear windows and consistent, well‑formed blades. Quality elements seat firmly and don’t bend excessively.
- Standards and markings: Preferred markings include amperage numbers and references to common automotive standards (e.g., SAE/ISO). Clear, legible printing reduces mix‑ups.
- Color accuracy: Standardized color coding helps quick ID; mismatched colors and ratings are a red flag.
- Organization aids: A compact, labeled case keeps fuses tidy. A built‑in chart, spare labels, and a fuse puller or small pliers are practical additions.
- High‑amperage coverage: Consider including a few main‑feed spares (e.g., maxi, JCASE, MIDI/ANL) if your vehicle uses them under the hood.
- Environmental resilience: For off‑road, marine, or high‑heat use, favor fuses and holders rated for the expected temperature and vibration levels.
- Beware of low‑quality imitations: Signs include inconsistent blade thickness, weak or brittle plastic, sloppy printing, incorrect color coding, and poor fit. Low‑grade fuses can run hot or fail unpredictably.
Placement, Storage & Readiness
Accessibility is everything. Store a labeled assortment where you can reach it quickly—not buried under cargo or exposed to heat and moisture.
- Best locations: Glovebox, center console, door pocket, or trunk toolkit near the jack. Keep a second set in your home garage if you maintain multiple vehicles.
- Include essential tools: Fuse puller, small needle‑nose pliers, flashlight, multimeter or test light, and your vehicle’s fuse diagram (print or photo).
- Protect from the elements: Use a snap‑shut case or resealable pouch; avoid leaving fuses loose where they can corrode or pick up grime.
- Label and inventory: Mark compartments by amperage. Replace used spares immediately so your kit stays complete.
- Maintenance cadence: Inspect annually. Make sure blades are clean, plastic isn’t warped, and the case hasn’t cracked from heat.
- Avoid common mistakes: Mixing different sizes in one unlabeled pocket, throwing fuses into the engine bay, or relying on color alone to choose amperage.
How to Use It Properly
- Park safely, switch off the engine, engage the parking brake, and remove the key. If working near the under‑hood box, let hot components cool.
- Consult the fuse diagram (owner’s manual or lid chart) to identify the correct fuse for the failed circuit.
- If appropriate and safe, disconnect the vehicle’s negative battery terminal to reduce the risk of accidental shorts while working.
- Use a fuse puller or small pliers to remove the suspect fuse straight out of its slot.
- Inspect the fuse element. If it’s broken, melted, or sooty, it’s likely blown. When uncertain, verify with a test light or multimeter for continuity.
- Match a replacement of the same physical type and amperage rating. Confirm by reading the printed number on the new fuse.
- Insert the new fuse firmly into the same slot. Ensure it seats fully and sits flush with neighboring fuses.
- Reconnect the battery (if disconnected) and test the circuit. Confirm the accessory or system operates normally.
- Monitor the circuit. If the new fuse blows immediately, stop. Repeated failures indicate a short or component fault that needs professional diagnosis.
- Record what happened and keep the blown fuse to show a technician if further repair is needed.
Safety reminders: Never install a higher‑amp fuse to “solve” a recurring blow, never bridge a fuse with metal, and do not service high‑voltage hybrid/EV fuses. When in doubt, consult a qualified technician. This guide is educational and does not replace your vehicle manufacturer’s instructions.
Final Summary
Car fuses are simple, reliable guardians of your vehicle’s electrical system. They prevent damage, reduce fire risk, and help you restore essential functions fast when something goes wrong. A small, well‑organized assortment tailored to your vehicle—paired with a basic puller, light, and fuse diagram—turns a frustrating roadside hiccup into a quick fix.
Prepare now: verify your vehicle’s fuse types and ratings, stock a complete set, and stage it in an easy‑to‑reach spot. With a few thoughtful steps today, you’ll be ready to protect your car, your trip, and your safety when the unexpected happens.
JOREST 280 Pcs Fuse Kit,182 Mini Car Fuses Assortment + 98 Standard Auto Blade Fuse, Replacement for Tool Automtive RV Motorcycle Truck Accessories(2A 3A 5A 7.5A 10A 15A 20A 25A 30A 35A 40AMP) Best for most families
- Restores 12V power to lights, radios, pumps, and charging after a blown circuit.
- Interrupts fault current, reducing overheating and vehicle fire risk.
- Standard ratings and colors enable fast, correct replacement under stress.
- Compact, nonperishable, and compatible with common automotive and 12V systems.